Solid-State Battery Materials – Sep 22
Solid-State Battery Materials - Sep 22
Chemistry
Saly Jose
Patented solid electrolytes enabling safer and more efficient next-generation batteries.
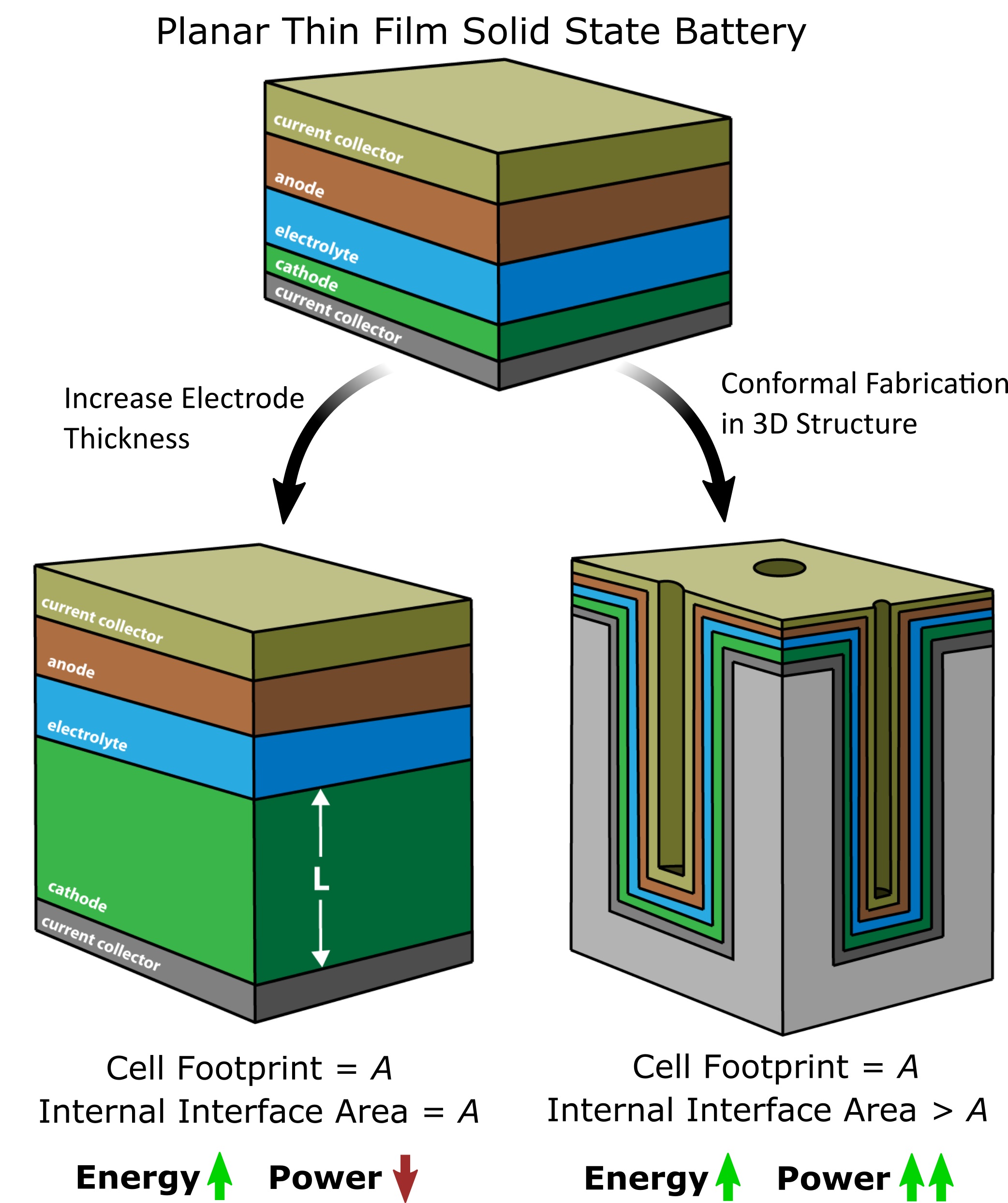
The patented solid electrolytes technology is a breakthrough innovation that enables the development of safer and more efficient next-generation batteries. Traditional lithium-ion batteries rely on liquid electrolytes, which can be prone to thermal runaway, leakage, and flammability. In contrast, solid electrolytes offer a more stable and secure alternative, with improved ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability.The patented solid electrolytes material boasts a unique crystal structure that facilitates high ionic conductivity, allowing for efficient charge transport and minimizing internal resistance. This results in improved battery performance, including enhanced discharge capacity, rate capability, and cycle life. Furthermore, the solid electrolytes exhibit excellent thermal stability, with a high melting point that prevents thermal runaway and reduces the risk of fires.The technology also enables the development of all-solid-state batteries, which eliminate the need for liquid electrolytes and separators. This design allows for increased energy density, as well as improved safety features such as reduced risk of leakage and enhanced mechanical stability. The all-solid-state battery architecture also enables more flexible and compact designs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from electric vehicles to consumer electronics.The patented solid electrolytes technology has been optimized for scalability and cost-effectiveness, with a manufacturing process that can be easily integrated into existing battery production lines. This enables the widespread adoption of safer and more efficient next-generation batteries, with significant potential impact on industries such as automotive, renewable energy, and consumer electronics. The technology's improved performance, safety, and sustainability features make it an attractive solution for companies seeking to develop more advanced and environmentally friendly battery solutions.
Electric vehicles: enabling faster charging, longer driving ranges, and reduced risk of battery fires, which can increase adoption rates and make EVs more competitive with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Renewable energy systems: allowing for more efficient and reliable storage of excess energy generated by solar panels and wind turbines, which can help stabilize the grid and enable greater integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Consumer electronics: powering smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices such as smartphones, laptops, and wearables, which can lead to longer battery life, faster charging, and new form factors.
Grid-scale energy storage: providing a safer and more efficient solution for large-scale energy storage, which can help utilities manage peak demand, stabilize the grid, and enable greater integration of renewable energy sources.
Aerospace and defense: enabling the development of more efficient and reliable batteries for electric aircraft, which can increase range, reduce emissions, and improve overall performance.
Medical devices: powering implantable medical devices such as pacemakers, which can benefit from the increased safety, efficiency, and reliability of solid-state batteries.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Proposal
View Patent