LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
Geoscience
Shubham Yadav
LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to create high-resolution 3D models of the earth's surface. It is used to study topography, monitor land use changes, and detect geological f
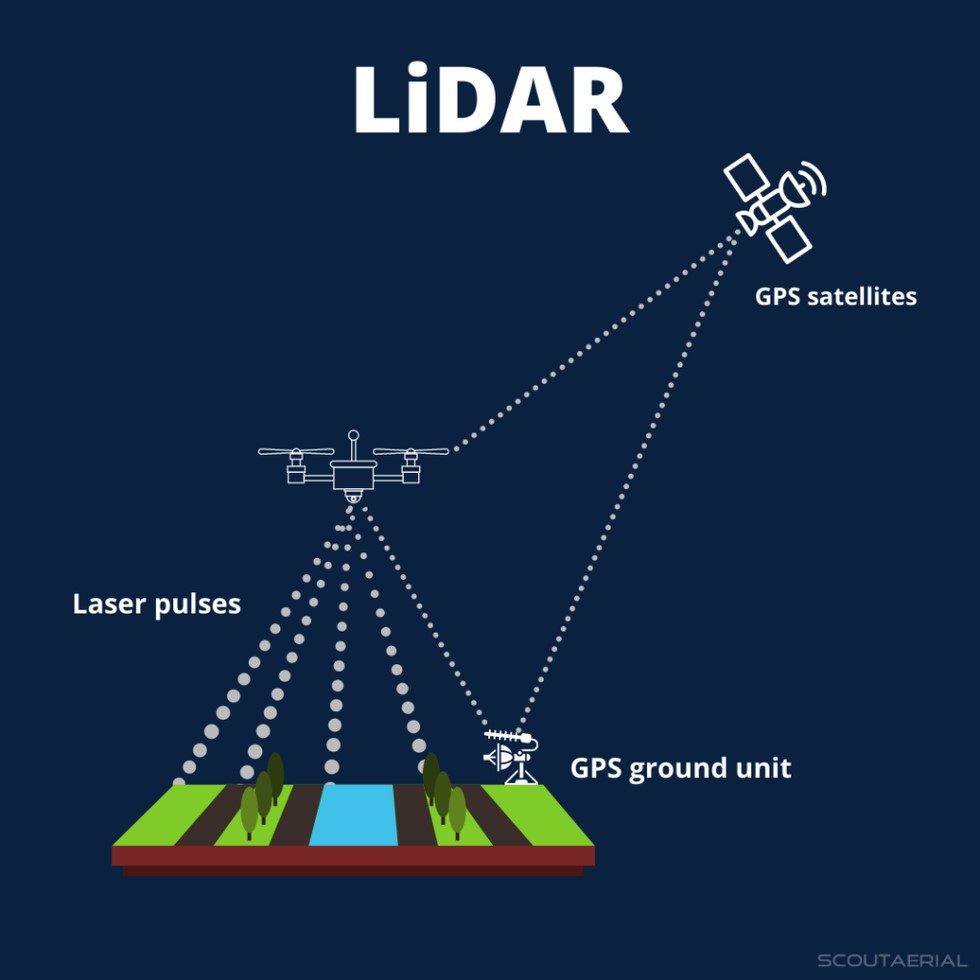
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that utilizes laser light to generate high-resolution three-dimensional models of the Earth's surface. The technology operates by emitting laser pulses towards the ground and measuring the time-of-flight and wavelength of the reflected signals. This process, also known as laser scanning, enables the creation of precise topographic maps and 3D models.The LiDAR system consists of several key components, including a laser scanner, GPS, and an inertial measurement unit (IMU). The laser scanner emits laser pulses and records the reflected signals, while the GPS and IMU provide location and orientation data for the system. The collected data is then processed using specialized software to create a point cloud, which is a set of 3D coordinates representing the reflected laser pulses.LiDAR technology has numerous applications in various fields, including topography, land use monitoring, and geological feature detection. In topography, LiDAR is used to create high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) that accurately represent the Earth's surface. This information is essential for understanding terrain characteristics, such as slope, aspect, and roughness.In land use monitoring, LiDAR data is used to detect changes in land cover, such as deforestation, urbanization, and soil erosion. The high-resolution 3D models generated by LiDAR enable researchers to track changes in land use patterns over time and assess the impacts of human activities on the environment. Additionally, LiDAR is used in geological feature detection to identify and characterize features such as faults, fractures, and landforms. The technology provides valuable insights into geological processes and helps researchers understand the underlying structure of the Earth's surface.
Mapping and surveying: LiDAR technology can be used to create accurate and detailed topographic maps, which is essential for urban planning, construction, and infrastructure development.
Land use monitoring: LiDAR can help monitor changes in land use patterns, such as deforestation, urbanization, and crop growth, which is crucial for environmental monitoring and management.
Geological hazard detection: LiDAR can be used to detect geological features such as faults, landslides, and subsidence, which can help identify areas prone to natural hazards.
Environmental monitoring: LiDAR can be used to monitor environmental changes such as glacier melting, sea level rise, and coastal erosion.
Autonomous vehicles: LiDAR technology is used in autonomous vehicles to detect and respond to their surroundings, enabling them to navigate safely and efficiently.
Forestry management: LiDAR can be used to create detailed 3D models of forests, which can help estimate tree height, biomass, and canopy density.
Coastal zone management: LiDAR can be used to monitor coastal erosion, track changes in shoreline morphology, and identify areas vulnerable to flooding.
Disaster response and recovery: LiDAR can be used to quickly assess damage and identify areas of need after a natural disaster.
Infrastructure inspection: LiDAR can be used to inspect and monitor the condition of infrastructure such as bridges, roads, and buildings.
Archaeological research: LiDAR can be used to create detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, which can help researchers better understand the layout and structure of ancient settlements.
United Nations Organization (UN), World Health Organization (WHO)
Proposal, Data
View Patent